The amount of assets, valuable items and resources owned by an individual, firm or any country or group. Wealth is usually applied to generate an income for the owners.
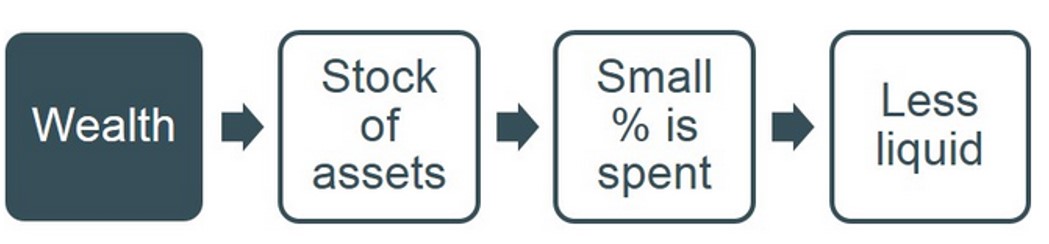
Below highglights some of the basic features of wealth. For instance wealth is the accumlation of value of assets and as a result very little of a person's wealth is spent, with the main reason being because it is less liquid and primarily income is used for day to day transactions.