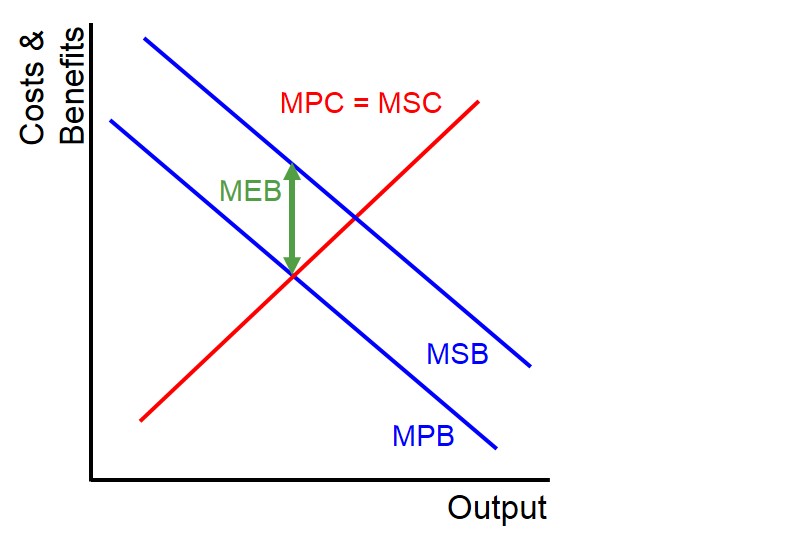
The additional benefit imposed on third parties by the consumption of an extra unit of a good or service. The benefit may be negative or positive.
Below is a diagram to highlight the external benefit that is present in a market with a positive consumption externality. This measures the size of the external benefit that will be realised from third-parties if the amount of goods consumed rises to the socially optimal amount i.e. it is the opposite of a dead weight loss triangle. In this instance the marginal external benefit exists because there is a divergence between the marginal private benefit and the marginal social benefit curves.