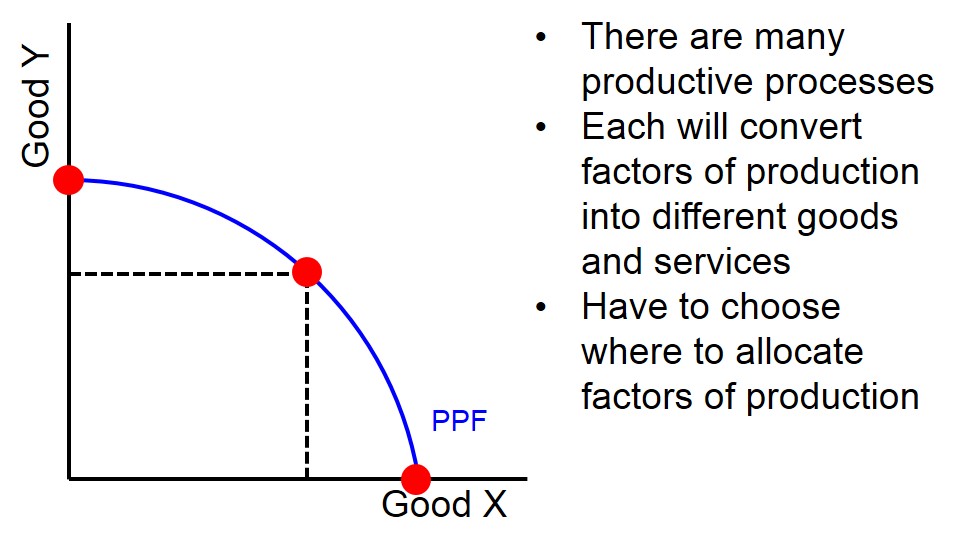
A convex curve that joins all possible combinations of output when all resources are fully engaged in production.
The diagram below shows the basic shape of a country's PPF, illustrating the the distribution and allocation of resources towards producing goods to help the economy achieve the full employment level of output. Any point on the PPF is a point that is pareto optimal, productively and allocatively efficient due to the utilisation of all the factors of prodcution in the economy.