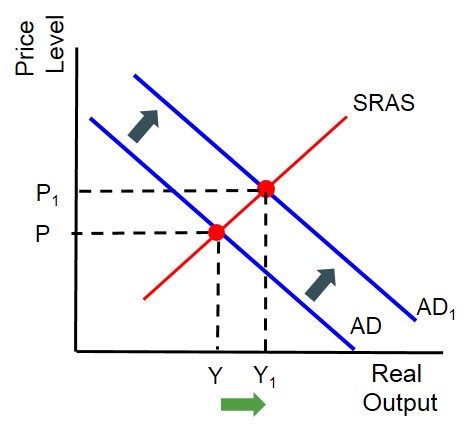
When an economy grows after a period of contraction.
Often these types of recoveries are stimulated by government policies e.g. an interest rate cut, a batch of quantitatitve easing, cut in taxation or higher government spending. All these policies aim to move the economy back towards full employment. Below is a diagram which highlight the effects that these types of policies can have on the economy in an AD-AS framework.